The Power BI service, gateway connection
It’s not uncommon to have data living in multiple locations in your organization. Data in your data center, data in the cloud, etc. Since these types of data stores are directly managed usually by your internal IT folks, on your main network domain, and easily accessible, they tend to pose no issue when needing to access them via reporting and analytics tools. But what about that legacy database sitting at your Nebraska warehouse? Or that remote international site? How do you add this data to the mix? You need the Power BI on-premises data gateway!
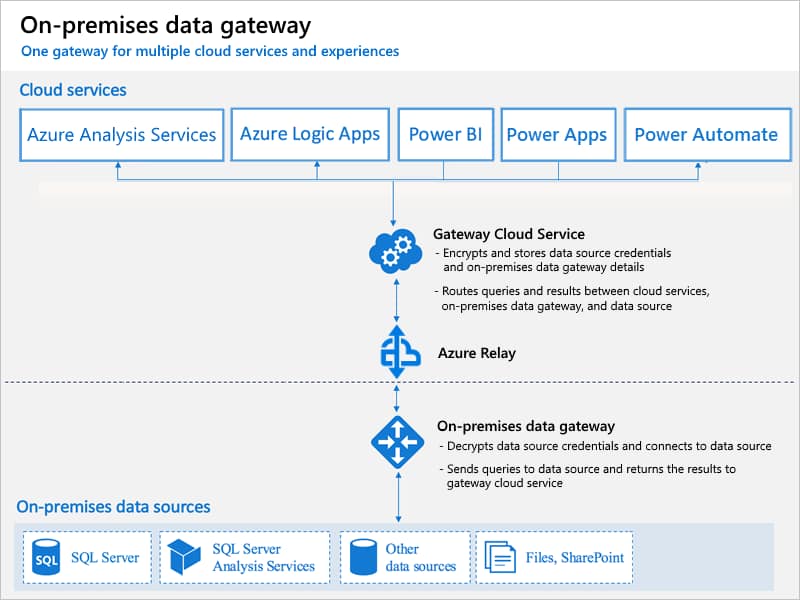
The on-premises data gateway acts as a bridge to provide quick and secure data transfer between on-premises data (data that isn’t in the cloud) and several Microsoft cloud services. These cloud services include Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, Azure Analysis Services and Azure Logic Apps. By using a gateway, you can keep databases and other data sources on your on-premises networks, yet securely use that on-premises data in cloud services.
To understand the Power BI gateway, you first need to understand how Microsoft has structured its vendor hosted Power BI service (app.powerbi.com). Instead of installing application servers locally or installing an application on a server running in the cloud, Power BI service is fully managed and hosted by Microsoft on its Azure cloud stack.
This architecture means that any published report that needs access to data on your local or corporate network will need a way to securely access that information. This is where Power BI gateway comes in.
Power BI gateway enables Power BI service to securely reach back into your network for data to display in Power BI service.
To see a video and demos of this content, watch our on-demand webinar Power BI Gateway: Understanding, Installing, Configuring.
Configuration best practices
You will need to install the Power BI gateway on one or more computers on your network. In an enterprise environment, we recommend setting up a development gateway server and production gateway server. This practice allows you to test out the monthly gateway software updates and configure new data sources without risk to your production environment. However, these gateways will both connect to your same Power BI service.
Microsoft thinks of these gateways as clusters. By default, you have a 1-node cluster of each gateway when you install it. You can add additional gateway machines to an existing cluster for higher redundancy and load balancing.
The Power BI gateway supports both importing data on a schedule and running live queries against your local data sources, a capability Microsoft refers to as DirectQuery. If your organization heavily uses DirectQuery, you should consider running a 2- or more-node cluster for both uptime and performance reasons.
Installation and upgrading
After the Power BI gateway software is downloaded and installed, it will run as a service. By default, it will start running under a dedicated local service account. We recommend you configure a specific domain user account for this service so that permissions can be managed by IT at a domain level, assuming you do this for other service level accounts in your organization.
The application will walk you through logging into Power BI service to add your gateway to a new or existing cluster. We also recommend turning on the HTTPS mode on the Network tab to encrypt your data at all times. Once complete, your gateway will be online and ready for use.
Data source setup and permissions
Data sources can be set up in Power BI service that rely on the on-premise remote data sources. When reports are published that reference on-premise data sources, Power BI service will be able to securely reach back into your network for fresh data.
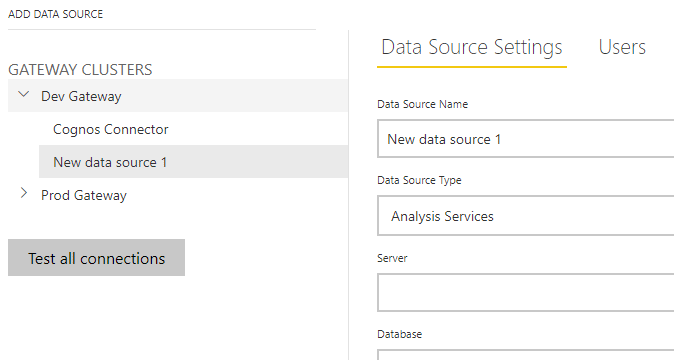
After navigating to the Manage gateways page in Power BI service, you will see a list of your installed clusters. You can then add data sources to each gateway cluster, supplying the data source type and authentication information. The Users tab allows for specific users or security groups to be granted access to the data source for their published reports.
Data sources single sign on
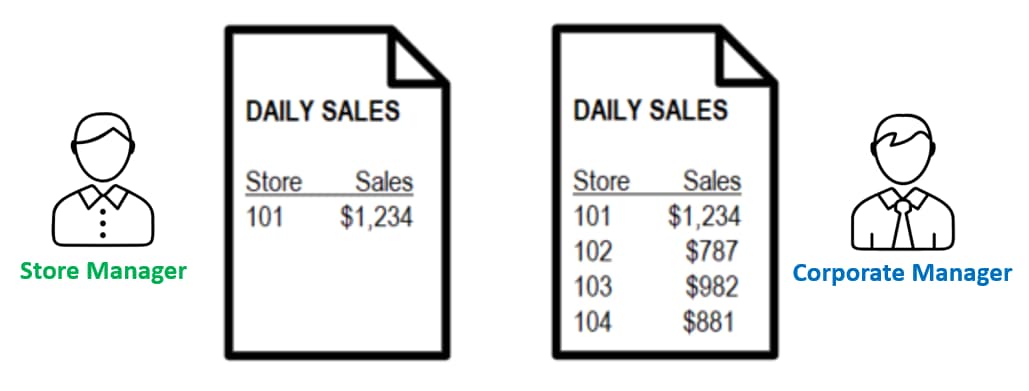
The Power BI gateway can also pass authentication information to the data sources your users will connect to. This means row-level security for users will be enforced at the data warehouse layer because that DW knows who they are. This task is typically accomplished using Kerberos and is supported by a subset of Power BI data sources. If your data warehouse supports it, and your team manages RLS at the data warehouse level, the end result is that users viewing reports on Power BI service will only see the slices of data they have access to. For example, a store manager would only see information about their store, but a corporate manager would see information about all stores.
Related considerations
There are some technical limitations and things to watch out for when installing and using the gateway:
- Gateways aren’t supported on Server Core installations.
- Gateways aren’t supported on Windows containers.
- The user installing the gateway must be the admin of the gateway.
- The gateway can’t be installed on a domain controller.
- If you’re planning to use Windows authentication, make sure you install the gateway on a computer that’s a member of the same Active Directory environment as the data sources.
- Don’t install a gateway on a computer, like a laptop, that might be turned off, asleep or disconnected from the Internet. The gateway can’t run under any of those circumstances.
- If a gateway uses a wireless network, its performance might suffer.
- If you use a virtualization layer for your virtual machine, performance might suffer or perform inconsistently. Set the gateway on a wired device for best network performance.
- You could install other applications on the gateway machine, but these applications might degrade gateway performance. If you do install other applications on the gateway machine, be sure to monitor the gateway closely to check if there’s any resource contention.
- You can install up to two gateways on a single computer: one running in personal mode and the other running in standard mode. An on-premises data gateway (personal mode) can be used only with Power BI. You can’t have more than one gateway running in the same mode on the same computer.
- The on-premises data gateway (standard mode) must be installed on a domain joined machine having a trust relationship with the target domain.
Power BI gateway summed up
Power BI gateway is a vital component in any enterprise level Power BI deployment. Considerations around development and production environments, user accounts, VM sizing and redundancy need to be considered when deploying a Power BI gateway.
Sound daunting?
If installing, configuring and optimizing Power BI sounds a bit daunting, it is. But don’t let that deter you. Senturus can help. We provide support when and how you need it. Contact us.